Abstract
Background:
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a common cause of morbidity and mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) despite major advances in diagnostic techniques and antiviral prophylactic strategies. The relative impacts of donor/recipient CMV serologic status, disease-specific and transplant-related prognostic factors on the risk of CMV reactivation and survival are undefined.
Methods:
We studied the outcome of 199 patients (median age, 46 years; range 17-71 years) receiving allogeneic HCT at National University Cancer Institute of Singapore (NCIS) between January 2016 and December 2020. Their hematologic diseases included AML (n=92), ALL (n=46), MDS (n=19), lymphomas (n=19), MPN (n=7) and others (n=16) such as refractory myelomas and aplastic anemias. The conditioning regimens used were either myeloablative (n=80) or reduced intensity conditioning (n=119) prior to an allograft from different donor sources. T-cell depletion (TCD) was used for GVHD prophylaxis in 124 patients; and this included post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy, n=31), ex-vivo T-cell receptor alpha-beta / CD45RA depletion (TCRab/CD45RA) (ex-vivo TCD, n=31) for haploidentical HCT, or thymoglobulin (ATG, n=62) for matched unrelated donor (MUD) HCT.
Results:
With a median follow-up duration of 15.6 months (range, 0.2-63.6 months), 136 (68.3%) patients had CMV reactivation (median onset, 27.5 days) while 6 (3.0 %) patients developed clinically significant CMV disease, such as colitis, retinitis and encephalitis. The cumulative incidences of CMV reactivation within the first 100 days among the recipients of matched unrelated donor (MUD) (n=60), mismatched related donor or unrelated donor (MMRD/MMUD) (n=60), umbilical cord blood (UCB) (n=18) and matched related donor (MRD) (n=61) HCT were 71.6 %, 61.7 %, 50.0 % and 32.7 %, respectively (p<0.001).
There were no statistically significant differences in overall survival (OS, p=0.830) and disease-free survival (DFS, p=0.983) at 5 years between CMV-seropositive (D+/R+ or D-/R+, n=181) and CMV-seronegative recipients (D-/R- or D+/R-, n=18). There were also no significant differences in the cumulative incidences of CMV reactivation within 100 days (p=0.879), CMV end-organ disease (p=0.522) and non-relapse mortality (NRM, p=0.202), respectively. HCT-CI score of ≥1 (p=0.005) and the use of reduced intensity conditioning regimen (p<0.001) were associated with a higher NRM at 2 years. There was also a trend towards higher NRM among patients with peak CMV DNA titers of above 1000 IU/ml, but this did not reach statistical significance (p=0.188).
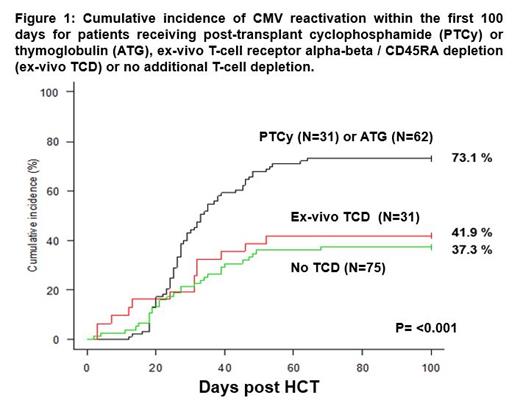
The secondary objective of this study was to determine the risk factors associated with CMV reactivation within the first 100 days post-transplant. There was no statistically significant impact of the donor or recipient CMV serostatus (p=0.790) on the risk of CMV reactivation. In multivariable analysis, the use of any T-cell depletion (p<0.001) was a significant predictor of CMV reactivation. In a subset analysis comparing the 3 different methods of TCD, the use of ATG (p=0.004) and PTCy (p=0.005) was found to be associated with an increased risk of CMV reactivation, but not in patients receiving ex-vivo TCD (p=0.184) (Figure 1). Notably, patients receiving ex-vivo TCD haploidentical HCT was not associated with a higher risk of CMV reactivation as compared to the recipients of MRD HCT without any TCD.
Conclusions:
Our study concluded that CMV serologic status did not affect the incidence of CMV reactivation, NRM, OS and DFS in patients undergoing allogeneic HCT. The use of PTCy and ATG for GVHD prophylaxis, remains the most important risk factor for CMV reactivation in the era of pre-emptive therapy and hence, the need for aggressive prevention strategies in this vulnerable group of patients.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal